Center for Computational & Data Sciences
Exploring Nature and Society Through Data & Computation






Exploring Nature and Society Through Data & Computation
Discovering secrets of nature’s wonders through computational insights and data-driven exploration.
Transforming society through the power of computational analysis and data-driven solutions.
Unraveling the hidden stories within data, fueling innovation and driving decision-making.
Unleashing the potential of computation to tackle complex challenges and shape a better future.
 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/596493148_1257195316449893_3887408594556244508_n-scaled.jpg
987
2560
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-12-09 07:55:002025-12-09 07:55:00CCDS wins Best Paper and Best Presenter Awards at 2025 IEEE SCOReD in Malaysia
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/596493148_1257195316449893_3887408594556244508_n-scaled.jpg
987
2560
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-12-09 07:55:002025-12-09 07:55:00CCDS wins Best Paper and Best Presenter Awards at 2025 IEEE SCOReD in Malaysia https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/588472913_862637909613335_5488227795735314575_n.jpg
553
1382
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-11-24 07:33:592025-12-09 07:37:46One of our research papers have been accepted at WACV 2026
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/588472913_862637909613335_5488227795735314575_n.jpg
553
1382
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-11-24 07:33:592025-12-09 07:37:46One of our research papers have been accepted at WACV 2026 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/586022512_860371103173349_4915657824356666621_n.jpg
1222
1776
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-11-21 07:27:442025-12-09 07:33:08Team THREE Makes History with 1st Place Win at 3MT Bangladesh 2025
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/586022512_860371103173349_4915657824356666621_n.jpg
1222
1776
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-11-21 07:27:442025-12-09 07:33:08Team THREE Makes History with 1st Place Win at 3MT Bangladesh 2025 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Screenshot-2025-12-09-132453.png
368
730
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-22 06:49:432025-12-09 12:22:06Two of our research papers have been accepted at EMNLP 2025
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Screenshot-2025-12-09-132453.png
368
730
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-22 06:49:432025-12-09 12:22:06Two of our research papers have been accepted at EMNLP 2025 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/535006063_781744904369303_7361255283533209095_n.jpg
594
480
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-18 20:19:032025-08-18 20:20:03CCDS Alumni(senior project student) Sadia Khan Receives Fully Funded Scholarship for Master’s at Uppsala
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/535006063_781744904369303_7361255283533209095_n.jpg
594
480
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-18 20:19:032025-08-18 20:20:03CCDS Alumni(senior project student) Sadia Khan Receives Fully Funded Scholarship for Master’s at Uppsala https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/500227053_715589370984857_2720183648371422814_n.jpg
424
512
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 22:20:102025-08-10 18:12:32Two papers accepted at the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP 2025)
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/500227053_715589370984857_2720183648371422814_n.jpg
424
512
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 22:20:102025-08-10 18:12:32Two papers accepted at the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP 2025) https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Screenshot-2025-06-15-123952.png
367
739
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 22:01:552025-08-10 18:12:32Two CCDS RAs (Jahir Sadik Monon and Rakibul Hasan Rajib) got US visa
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Screenshot-2025-06-15-123952.png
367
739
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 22:01:552025-08-10 18:12:32Two CCDS RAs (Jahir Sadik Monon and Rakibul Hasan Rajib) got US visa https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/487297818_673630788514049_6424296810912772183_n.jpg
524
1280
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:41:282025-08-10 18:12:33Group photo of CSE, IUB faculty members who are part of CCDS
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/487297818_673630788514049_6424296810912772183_n.jpg
524
1280
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:41:282025-08-10 18:12:33Group photo of CSE, IUB faculty members who are part of CCDS https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Screenshot-2025-07-29-023912.png
700
1090
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:39:482025-08-10 18:12:33Our paper got accepted to CHI (the Top Ranked Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems) 2025’s Late Breaking Work Track!
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Screenshot-2025-07-29-023912.png
700
1090
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:39:482025-08-10 18:12:33Our paper got accepted to CHI (the Top Ranked Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems) 2025’s Late Breaking Work Track! https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481248473_658222566721538_8110864968781209685_n.jpg
1535
2048
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:30:062025-08-10 18:12:332nd CCDS Workshop on Deep Learning Code Management
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481248473_658222566721538_8110864968781209685_n.jpg
1535
2048
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:30:062025-08-10 18:12:332nd CCDS Workshop on Deep Learning Code Management https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Screenshot-2025-07-29-022501.png
472
760
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:25:532025-08-10 18:12:33Announcement of the Interdisciplinary Computational Biology workshop 2025
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Screenshot-2025-07-29-022501.png
472
760
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:25:532025-08-10 18:12:33Announcement of the Interdisciplinary Computational Biology workshop 2025 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/482071628_657693340107794_8570280266799986507_n.jpg
1280
960
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:23:312025-08-10 18:12:34Congratulations to Muhtasim Ibteda and Ashfaq for completing their senior project.
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/482071628_657693340107794_8570280266799986507_n.jpg
1280
960
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:23:312025-08-10 18:12:34Congratulations to Muhtasim Ibteda and Ashfaq for completing their senior project.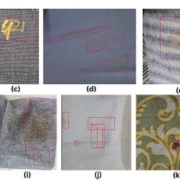 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481081666_657693276774467_6918765723561964024_n.jpg
475
1062
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:20:192025-08-10 18:12:34Congratulations to Farzana Islam, Sumaya, Md. Fahad Monir, and Dr Ashraful Islam for getting their paper accepted in Data in Brief, Elsevier.
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481081666_657693276774467_6918765723561964024_n.jpg
475
1062
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:20:192025-08-10 18:12:34Congratulations to Farzana Islam, Sumaya, Md. Fahad Monir, and Dr Ashraful Islam for getting their paper accepted in Data in Brief, Elsevier.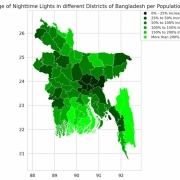 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481664924_657687866775008_7530161650518040295_n.jpg
705
880
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:18:192025-08-10 18:12:34A paper has been accepted for publication in the Journal of the Asia Pacific Economy
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481664924_657687866775008_7530161650518040295_n.jpg
705
880
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:18:192025-08-10 18:12:34A paper has been accepted for publication in the Journal of the Asia Pacific Economy https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/482059915_657687393441722_9212931300867946223_n.jpg
818
1075
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:15:062025-08-10 18:12:34Two Groups of our BSc Senior Project Students of HCI Wing have been selected for Innovation Cohort of the LaunchPad by the University Innovation Hub Program (UIHP) at UIU!
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/482059915_657687393441722_9212931300867946223_n.jpg
818
1075
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:15:062025-08-10 18:12:34Two Groups of our BSc Senior Project Students of HCI Wing have been selected for Innovation Cohort of the LaunchPad by the University Innovation Hub Program (UIHP) at UIU! https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481079885_657685723441889_1839993065073548081_n.jpg
720
511
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:10:492025-08-10 18:12:35We are excited to offer research internship positions
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481079885_657685723441889_1839993065073548081_n.jpg
720
511
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:10:492025-08-10 18:12:35We are excited to offer research internship positions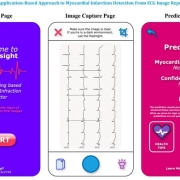 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481667566_657443196799475_8138819820331588582_n.jpg
391
600
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:07:382025-08-10 18:12:35Two papers by CCDS Senior RAs have been accepted at the prestigious IEEE 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), USA!
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481667566_657443196799475_8138819820331588582_n.jpg
391
600
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:07:382025-08-10 18:12:35Two papers by CCDS Senior RAs have been accepted at the prestigious IEEE 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), USA! https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/465104182_571095052100957_210695626144326625_n-e1730288585915.jpg
411
576
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:01:572025-08-10 18:12:35Dr AKM Mahbubur Rahman presents out paper in one of the reputed AI conferences, ECAI
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/465104182_571095052100957_210695626144326625_n-e1730288585915.jpg
411
576
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 20:01:572025-08-10 18:12:35Dr AKM Mahbubur Rahman presents out paper in one of the reputed AI conferences, ECAI https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481227164_657440936799701_736766488209624797_n.jpg
960
945
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 19:59:212025-08-10 18:12:36Big congrats to our CCDS RA Farhan Israk Soumik for starting his fully funded PHD journey in Computer Science program at Southern Illinois University, Carbondale.
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481227164_657440936799701_736766488209624797_n.jpg
960
945
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 19:59:212025-08-10 18:12:36Big congrats to our CCDS RA Farhan Israk Soumik for starting his fully funded PHD journey in Computer Science program at Southern Illinois University, Carbondale.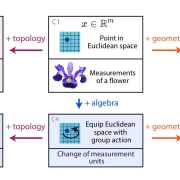 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481219833_657432926800502_3088526591238091847_n.jpg
631
1434
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 19:56:012025-08-10 18:12:36Beyond Euclid: An Illustrated Guide to Modern Machine Learning with Geometric, Topological, and Algebraic Structure, by Sanborn et al.
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481219833_657432926800502_3088526591238091847_n.jpg
631
1434
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 19:56:012025-08-10 18:12:36Beyond Euclid: An Illustrated Guide to Modern Machine Learning with Geometric, Topological, and Algebraic Structure, by Sanborn et al. https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481459213_657425776801217_943527840102543761_n.jpg
1200
1600
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 19:49:342025-08-10 18:12:36First undergrad group complete their senior project from the HCI wing.
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481459213_657425776801217_943527840102543761_n.jpg
1200
1600
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 19:49:342025-08-10 18:12:36First undergrad group complete their senior project from the HCI wing. https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481459463_657221660154962_5048915427098004500_n.jpg
288
600
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 19:44:272025-08-10 18:14:09CCDS student James selected for the CERN Summer Student Program 2024
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481459463_657221660154962_5048915427098004500_n.jpg
288
600
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 19:44:272025-08-10 18:14:09CCDS student James selected for the CERN Summer Student Program 2024 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Screenshot-2025-07-29-013812.png
262
272
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 19:38:412025-08-10 18:14:095 papers from CCDS has been accepted in ICPR 2024
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Screenshot-2025-07-29-013812.png
262
272
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 19:38:412025-08-10 18:14:095 papers from CCDS has been accepted in ICPR 2024 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/ECAI2024.jpg
389
800
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 19:27:532025-08-10 18:14:10One paper has been accepted in ECAI 2024
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/ECAI2024.jpg
389
800
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 19:27:532025-08-10 18:14:10One paper has been accepted in ECAI 2024 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481003405_657218320155296_7554872026654115885_n.jpg
348
595
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 19:21:552025-08-10 18:14:101st CCDS Summer School on Random Matrix Theory
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481003405_657218320155296_7554872026654115885_n.jpg
348
595
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 19:21:552025-08-10 18:14:101st CCDS Summer School on Random Matrix Theory https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Capture.png
702
700
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 17:44:062025-08-10 18:14:10Undergraduate Project Update Presentation Day
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Capture.png
702
700
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 17:44:062025-08-10 18:14:10Undergraduate Project Update Presentation Day https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/images.jpeg
225
225
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 17:40:322025-08-10 18:14:11Five Papers Accepted in EMBC 2024
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/images.jpeg
225
225
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 17:40:322025-08-10 18:14:11Five Papers Accepted in EMBC 2024 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
0
0
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 17:31:452025-08-10 18:14:11DPS IUB Summer School 2024: Glimpses into the Quantum World- Information, Technology, and Applications
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
0
0
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 17:31:452025-08-10 18:14:11DPS IUB Summer School 2024: Glimpses into the Quantum World- Information, Technology, and Applications https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481457212_652823180594810_7695058655942214804_n.jpg
854
2048
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 17:18:332025-08-10 18:14:11CCDS arranged a 3 day workshop on Systematic Literature Review
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/481457212_652823180594810_7695058655942214804_n.jpg
854
2048
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 17:18:332025-08-10 18:14:11CCDS arranged a 3 day workshop on Systematic Literature Review https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/ska-anim-1-scaled-1.jpg
463
1029
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 17:11:372025-08-10 18:14:11Hiring Research Assistant in Astronomy & Astrophysics
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/ska-anim-1-scaled-1.jpg
463
1029
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 17:11:372025-08-10 18:14:11Hiring Research Assistant in Astronomy & Astrophysics https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Dr._Md_Zahangir_Alam_.png
600
600
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 17:07:392025-08-10 18:14:12CCDS supervisor received grant from SR, IUB
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Dr._Md_Zahangir_Alam_.png
600
600
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 17:07:392025-08-10 18:14:12CCDS supervisor received grant from SR, IUB https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/A7X08863_1_-d40aaf33-da47-4189-b294-aaac3b247956.png
1088
1088
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 17:06:282025-08-10 18:14:12CCDS supervisor received grant from SR, IUB
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/A7X08863_1_-d40aaf33-da47-4189-b294-aaac3b247956.png
1088
1088
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 17:06:282025-08-10 18:14:12CCDS supervisor received grant from SR, IUB https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/MdFahim-e1720509136335.jpg
304
304
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 17:03:112025-08-10 18:14:12CCDS RA received “Best Shared Task Paper” in BanglaNLP workshop @EMNLP23
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/MdFahim-e1720509136335.jpg
304
304
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 17:03:112025-08-10 18:14:12CCDS RA received “Best Shared Task Paper” in BanglaNLP workshop @EMNLP23 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/download.png
225
225
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 16:58:232025-08-10 18:14:12Paper accepted in NeurIPS 2023 at 3rd Workshop on Efficient Natural Language and Speech Processing
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/download.png
225
225
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 16:58:232025-08-10 18:14:12Paper accepted in NeurIPS 2023 at 3rd Workshop on Efficient Natural Language and Speech Processing https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/ACM-SIGCHI.png
743
1145
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 16:51:342025-08-10 18:14:13Two of Our Undergrad Research Students Got Accepted to ACM SIGHCI Winter School
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/ACM-SIGCHI.png
743
1145
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 16:51:342025-08-10 18:14:13Two of Our Undergrad Research Students Got Accepted to ACM SIGHCI Winter School https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/unnamed-1-1.png
196
586
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 16:44:562025-08-10 18:14:13Paper Accepted at 15th International Conference on Intelligent Human-Computer Interaction, South Korea
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/unnamed-1-1.png
196
586
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 16:44:562025-08-10 18:14:13Paper Accepted at 15th International Conference on Intelligent Human-Computer Interaction, South Korea https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Bangla_Error_Corrector.png
547
597
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 16:42:172025-08-10 18:14:14Five Papers Accepted in BLP Workshop @EMNLP 2023
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Bangla_Error_Corrector.png
547
597
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-28 16:42:172025-08-10 18:14:14Five Papers Accepted in BLP Workshop @EMNLP 2023
 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Ajmain-e1762981885484.jpg
857
857
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-11-12 21:14:182025-11-12 21:14:18Md Ajmain Mahtab
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Ajmain-e1762981885484.jpg
857
857
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-11-12 21:14:182025-11-12 21:14:18Md Ajmain Mahtab https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/WhatsApp-Image-2025-11-24-at-23.06.34_aafb1d45-e1764004158358.jpg
312
312
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-11-12 21:09:112025-11-24 17:10:29Manosh Sur Choudhury
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/WhatsApp-Image-2025-11-24-at-23.06.34_aafb1d45-e1764004158358.jpg
312
312
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-11-12 21:09:112025-11-24 17:10:29Manosh Sur Choudhury https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Faiyaz_Picture-e1762980951848.jpg
446
412
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-11-12 20:55:162025-11-12 21:03:45Md. Faiyaz Abdullah Sayeedi
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Faiyaz_Picture-e1762980951848.jpg
446
412
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-11-12 20:55:162025-11-12 21:03:45Md. Faiyaz Abdullah Sayeedi https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/1000022999-scaled-e1763999159926.jpg
1920
1920
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-10-26 21:40:372025-11-24 15:46:19Halima Khatun
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/1000022999-scaled-e1763999159926.jpg
1920
1920
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-10-26 21:40:372025-11-24 15:46:19Halima Khatun https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/R103209-e1763999309890.jpg
471
471
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-10-26 21:26:132025-11-24 15:48:50Mir Sazzat Hossain
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/R103209-e1763999309890.jpg
471
471
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-10-26 21:26:132025-11-24 15:48:50Mir Sazzat Hossain https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/cv-photo-Picsart-BackgroundRemover.jpg
890
899
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-10-26 20:49:152025-10-26 20:49:15Fatin Israq Tabib
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/cv-photo-Picsart-BackgroundRemover.jpg
890
899
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-10-26 20:49:152025-10-26 20:49:15Fatin Israq Tabib https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/WhatsApp-Image-2025-10-20-at-22.00.05_b0557e30-e1760987518107.jpg
120
120
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-10-19 18:49:172025-10-20 19:13:26Istiaq Ahmed
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/WhatsApp-Image-2025-10-20-at-22.00.05_b0557e30-e1760987518107.jpg
120
120
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-10-19 18:49:172025-10-20 19:13:26Istiaq Ahmed https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/ZinnatSultana2-e1729669172133.jpg
724
724
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-19 06:52:552025-07-19 06:52:57Zinnat Sultana
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/ZinnatSultana2-e1729669172133.jpg
724
724
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-19 06:52:552025-07-19 06:52:57Zinnat Sultana https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/profile_pic-e1752906670798.jpg
1200
1200
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-19 06:31:282025-07-19 06:31:29Meheraj Hossain
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/profile_pic-e1752906670798.jpg
1200
1200
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-19 06:31:282025-07-19 06:31:29Meheraj Hossain https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/fuad-e1720339682147.png
312
312
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-18 22:20:332025-07-18 22:20:34Tahmid Hasan Fuad
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/fuad-e1720339682147.png
312
312
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-18 22:20:332025-07-18 22:20:34Tahmid Hasan Fuad https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/39516236.jpeg
401
401
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-18 22:17:582025-07-18 22:18:57Shadman Rohan
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/39516236.jpeg
401
401
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-18 22:17:582025-07-18 22:18:57Shadman Rohan https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Nabarun-scaled-1.jpg
2560
2560
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-18 22:14:202025-07-18 22:14:21Nabarun Halder
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Nabarun-scaled-1.jpg
2560
2560
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-18 22:14:202025-07-18 22:14:21Nabarun Halder https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/MdFahim-e1720509136335.jpg
304
304
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-18 22:09:022025-07-18 22:09:38Md Fahim
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/MdFahim-e1720509136335.jpg
304
304
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-18 22:09:022025-07-18 22:09:38Md Fahim https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/IMG-20240119-WA00152-e1720339554368.jpg
549
549
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-18 22:05:132025-07-18 22:06:28Jahir Sadik Monon
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/IMG-20240119-WA00152-e1720339554368.jpg
549
549
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-18 22:05:132025-07-18 22:06:28Jahir Sadik Monon https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/IMG_4575-scaled-e1730130486170.jpeg
2176
2176
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-18 22:02:292025-07-18 22:06:04Armun Alam
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/IMG_4575-scaled-e1730130486170.jpeg
2176
2176
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-18 22:02:292025-07-18 22:06:04Armun Alam https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/main-scaled-e1720508769417-1.jpg
773
773
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-18 22:00:192025-07-18 22:00:21Akm Moshiur Rahman Mazumder
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/main-scaled-e1720508769417-1.jpg
773
773
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-18 22:00:192025-07-18 22:00:21Akm Moshiur Rahman Mazumder https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/prof_pic-e1752793313807.jpg
674
674
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-17 23:02:342025-11-11 19:47:36Md Akil Raihan Iftee
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/prof_pic-e1752793313807.jpg
674
674
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-17 23:02:342025-11-11 19:47:36Md Akil Raihan Iftee https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/1000178214-e1751323848107.jpg
1480
1480
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-06-30 22:50:582025-06-30 22:50:59Syed Mohaiminul Hoque
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/1000178214-e1751323848107.jpg
1480
1480
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-06-30 22:50:582025-06-30 22:50:59Syed Mohaiminul Hoque https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/suit_photo_close-e1751323191781.jpg
906
906
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-06-30 22:40:052025-06-30 22:40:37Rafat Hasan Khan
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/suit_photo_close-e1751323191781.jpg
906
906
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-06-30 22:40:052025-06-30 22:40:37Rafat Hasan Khan https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/PassportSizeImage-e1751231226551.jpg
449
449
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-06-29 21:06:052025-06-29 21:07:15Rakibul Hasan Rajib
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/PassportSizeImage-e1751231226551.jpg
449
449
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-06-29 21:06:052025-06-29 21:07:15Rakibul Hasan Rajib17 new research collaborations started in 2024
 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/463596652_1616514599300647_5452142768462437922_n.jpg
658
654
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 22:08:052025-08-08 13:01:54Muhammad E. H. Chowdhury, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/463596652_1616514599300647_5452142768462437922_n.jpg
658
654
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 22:08:052025-08-08 13:01:54Muhammad E. H. Chowdhury, PhD https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/citations.jpeg
192
192
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 22:04:542025-08-02 22:04:55Fahad Parvez Mahdi, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/citations.jpeg
192
192
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 22:04:542025-08-02 22:04:55Fahad Parvez Mahdi, PhD https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/rahat.jpg
705
705
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:56:162025-08-02 21:56:18Moinul Hossain Rahat, Ph.D
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/rahat.jpg
705
705
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:56:162025-08-02 21:56:18Moinul Hossain Rahat, Ph.D https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/nazmul-shahadat-e1721021803167.png
613
613
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:49:182025-08-02 21:49:19Nazmul Shahadat, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/nazmul-shahadat-e1721021803167.png
613
613
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:49:182025-08-02 21:49:19Nazmul Shahadat, PhD https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/usama-e1729275012261.png
330
330
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:48:152025-08-02 21:48:17Muhammad Usama Islam
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/usama-e1729275012261.png
330
330
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:48:152025-08-02 21:48:17Muhammad Usama Islam https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/admin-ajax-2.png
750
750
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:46:592025-08-02 21:47:01Mr. Syed Tangim Pasha
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/admin-ajax-2.png
750
750
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:46:592025-08-02 21:47:01Mr. Syed Tangim Pasha https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/moath-e1729274593394.jpeg
551
551
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:45:362025-08-02 21:45:37Moath Awawdeh, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/moath-e1729274593394.jpeg
551
551
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:45:362025-08-02 21:45:37Moath Awawdeh, PhD https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Mehedi_Hassan-scaled-e1754171044801.jpeg
684
684
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:44:232025-08-02 21:44:24Mehedi Hassan, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Mehedi_Hassan-scaled-e1754171044801.jpeg
684
684
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:44:232025-08-02 21:44:24Mehedi Hassan, PhD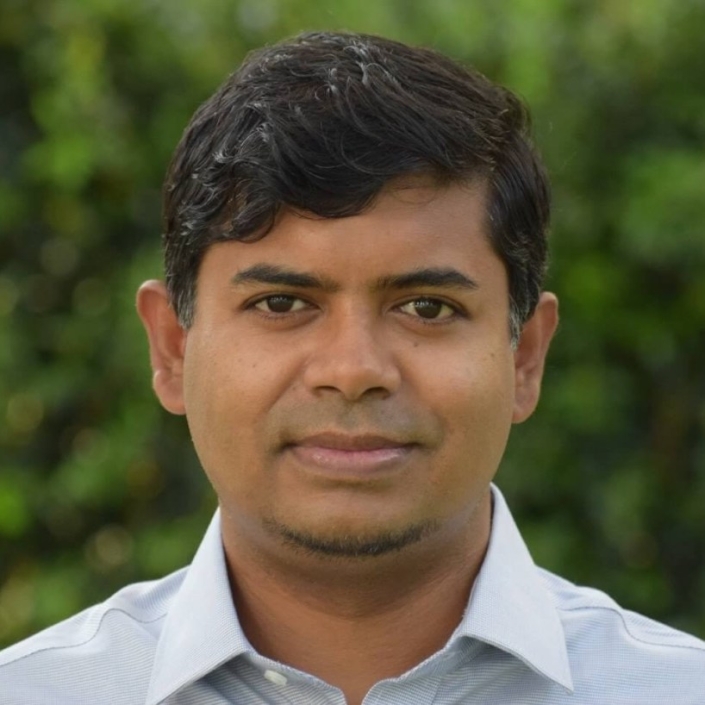 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Rakibul-e1720943843622.jpg
818
818
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:41:332025-08-02 21:41:35Md Rakibul Islam, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Rakibul-e1720943843622.jpg
818
818
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:41:332025-08-02 21:41:35Md Rakibul Islam, PhD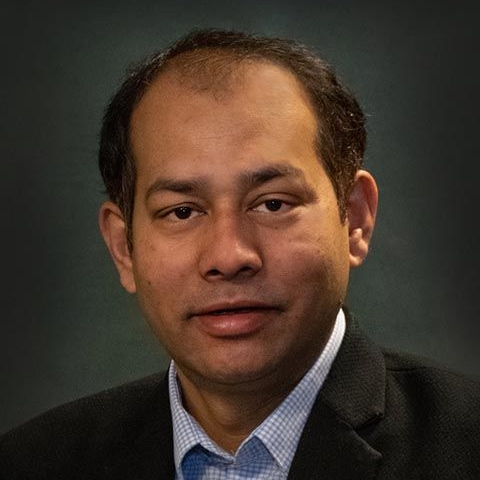 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/kabir-faisal-e1720511894189.jpg
480
480
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:39:032025-08-02 21:39:05Md Faisal Kabir, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/kabir-faisal-e1720511894189.jpg
480
480
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:39:032025-08-02 21:39:05Md Faisal Kabir, PhD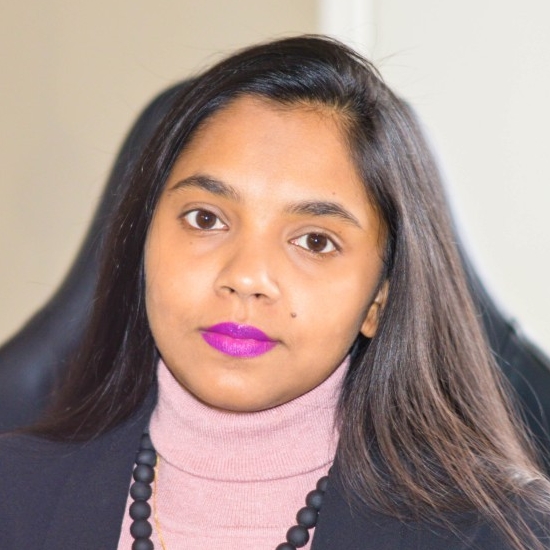 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Farzana-2-e1720945361842.jpg
550
550
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:36:142025-08-02 21:36:15Farzana Anowar, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Farzana-2-e1720945361842.jpg
550
550
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:36:142025-08-02 21:36:15Farzana Anowar, PhD https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Eshtiak-e1720942936908.png
315
315
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:34:522025-08-02 21:34:54Eshtiak Ahmed
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Eshtiak-e1720942936908.png
315
315
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:34:522025-08-02 21:34:54Eshtiak Ahmed https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Ishtiaque_edited-e1720944258949.jpg
127
127
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:32:572025-08-02 21:32:58Eshtiak Ahmed
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Ishtiaque_edited-e1720944258949.jpg
127
127
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:32:572025-08-02 21:32:58Eshtiak Ahmed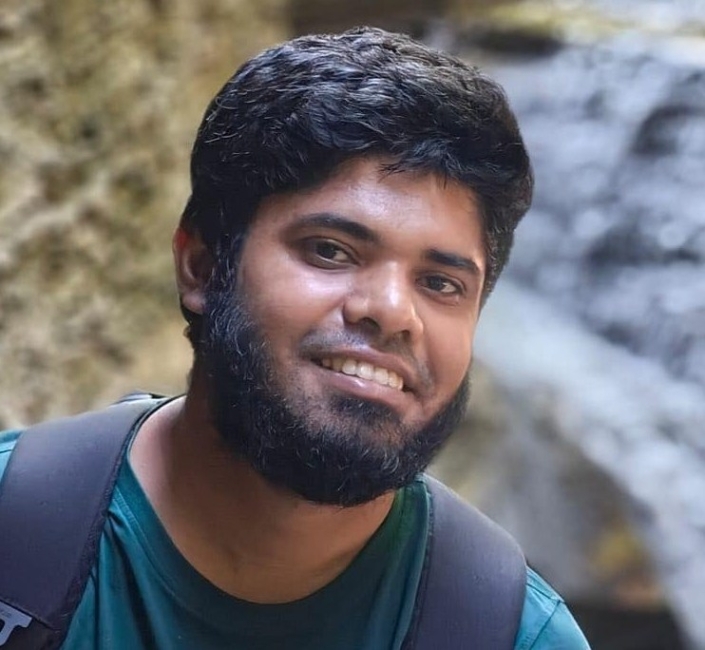 https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Ekram-e1729364372888.jpeg
684
742
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:30:222025-08-02 21:30:24Ekram Hossain
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Ekram-e1729364372888.jpeg
684
742
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:30:222025-08-02 21:30:24Ekram Hossain https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/admin-ajax-3-1.jpeg
1030
1030
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:28:562025-08-02 21:28:57D. M. Anisuzzaman, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/admin-ajax-3-1.jpeg
1030
1030
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:28:562025-08-02 21:28:57D. M. Anisuzzaman, PhD  https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/beenish-e1729273921371.png
641
641
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:26:082025-08-02 21:26:10Beenish Moalla Chaudhry, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/beenish-e1729273921371.png
641
641
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:26:082025-08-02 21:26:10Beenish Moalla Chaudhry, PhD https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Avdesh_Mishra_Pic-e1720511693929.jpg
487
487
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:22:452025-08-02 21:22:46Avdesh Mishra, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Avdesh_Mishra_Pic-e1720511693929.jpg
487
487
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-08-02 21:22:452025-08-02 21:22:46Avdesh Mishra, PhD https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/shibasaki.jpg
512
512
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-29 21:32:392025-07-29 21:32:39Shibasaki Ryosuke, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/shibasaki.jpg
512
512
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-29 21:32:392025-07-29 21:32:39Shibasaki Ryosuke, PhD https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/rumee.jpg
400
400
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-29 21:30:552025-07-29 21:30:58Sarkar Tanveer Ahmed Rumee, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/rumee.jpg
400
400
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-29 21:30:552025-07-29 21:30:58Sarkar Tanveer Ahmed Rumee, PhD https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/zaber.jpg
257
257
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-29 21:29:362025-08-06 12:05:54Moinul I Zaber, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/zaber.jpg
257
257
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-29 21:29:362025-08-06 12:05:54Moinul I Zaber, PhD https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/saikia.jpeg
200
200
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-29 21:23:572025-07-29 21:23:59Payaswini Saikia, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/saikia.jpeg
200
200
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-29 21:23:572025-07-29 21:23:59Payaswini Saikia, PhD https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/amit_portrait.png
601
554
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-29 21:20:502025-07-29 21:20:51Amitava Roy, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/amit_portrait.png
601
554
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-29 21:20:502025-07-29 21:20:51Amitava Roy, PhD https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/azad.jpeg
200
200
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-29 21:16:072025-07-29 21:16:10A K M Azad, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/azad.jpeg
200
200
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-29 21:16:072025-07-29 21:16:10A K M Azad, PhD https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/aman.jpg
256
246
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-29 21:14:352025-07-29 21:14:37Aman Chadha
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/aman.jpg
256
246
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-29 21:14:352025-07-29 21:14:37Aman Chadha https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/sajib-mistry-d41c64f3-1.jpg
746
746
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-29 21:13:112025-07-29 21:13:12Dr Sajib Mistry
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/sajib-mistry-d41c64f3-1.jpg
746
746
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-29 21:13:112025-07-29 21:13:12Dr Sajib Mistry https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/profile-1.jpg
300
300
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-29 21:10:152025-07-29 21:10:17Hasnain Heickal
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/profile-1.jpg
300
300
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-29 21:10:152025-07-29 21:10:17Hasnain Heickal https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Screenshot-2025-07-26-220951.png
316
316
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-26 16:10:332025-07-26 16:10:35Iftekhar Anam, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Screenshot-2025-07-26-220951.png
316
316
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-26 16:10:332025-07-26 16:10:35Iftekhar Anam, PhD https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Screenshot-2025-07-26-220207-e1753545779287.png
327
327
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-26 16:03:282025-07-26 16:03:30Ishtiaque Hussain, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Screenshot-2025-07-26-220207-e1753545779287.png
327
327
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-26 16:03:282025-07-26 16:03:30Ishtiaque Hussain, PhD https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/profile_pic-e1720944438515.jpg
599
599
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-26 15:56:422025-07-26 16:13:08Md Mofijul Islam
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/profile_pic-e1720944438515.jpg
599
599
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-26 15:56:422025-07-26 16:13:08Md Mofijul Islam https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/profile-scaled.jpg
2560
2560
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-26 13:29:272025-07-26 13:29:29Muntasir Wahed
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/profile-scaled.jpg
2560
2560
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-26 13:29:272025-07-26 13:29:29Muntasir Wahed https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/profile_pic_05-Mar-2018__04_03_22__1243863525.jpeg
130
120
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-26 13:22:012025-07-26 13:22:02Prof. M Shoyaib, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/profile_pic_05-Mar-2018__04_03_22__1243863525.jpeg
130
120
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-26 13:22:012025-07-26 13:22:02Prof. M Shoyaib, PhD https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Riashat.jpg
256
256
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-26 13:18:222025-07-26 13:18:24Riashat Islam, Ph.D | Student Researcher | Microsoft Research NYC and Microsoft Research Montreal
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Riashat.jpg
256
256
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-26 13:18:222025-07-26 13:18:24Riashat Islam, Ph.D | Student Researcher | Microsoft Research NYC and Microsoft Research Montreal https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Screen_Shot_2020_10_28_at_1.41.10_PM-e1753535739297.png
205
205
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-26 13:16:002025-07-26 13:16:01Ruhul Amin, PhD | Assistant Professor | Department of Computer and Information Science, Fordham University
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Screen_Shot_2020_10_28_at_1.41.10_PM-e1753535739297.png
205
205
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-26 13:16:002025-07-26 13:16:01Ruhul Amin, PhD | Assistant Professor | Department of Computer and Information Science, Fordham University https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/sidebar_thumb-e1753534703537.jpg
472
472
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-26 12:58:562025-07-26 12:58:57Saiful Islam, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/sidebar_thumb-e1753534703537.jpg
472
472
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-26 12:58:562025-07-26 12:58:57Saiful Islam, PhD https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/hassan-e1721023939251.jpg
154
154
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-26 12:50:082025-07-26 12:51:07Syeda Sakira Hassan, PhD
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/hassan-e1721023939251.jpg
154
154
Abu Hurairah Rifat
https://ccds.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/final-logo-09-1-300x109-2.png
Abu Hurairah Rifat2025-07-26 12:50:082025-07-26 12:51:07Syeda Sakira Hassan, PhDCenter for Computational & Data Sciences (CCDS), Independent University, Bangladesh (IUB).
Plot 16, Aftabuddin Ahmed Road, Block B, Bashnudhara RA, Dhaka 1229, Bangladesh.
