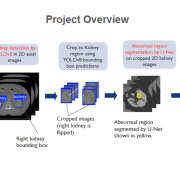
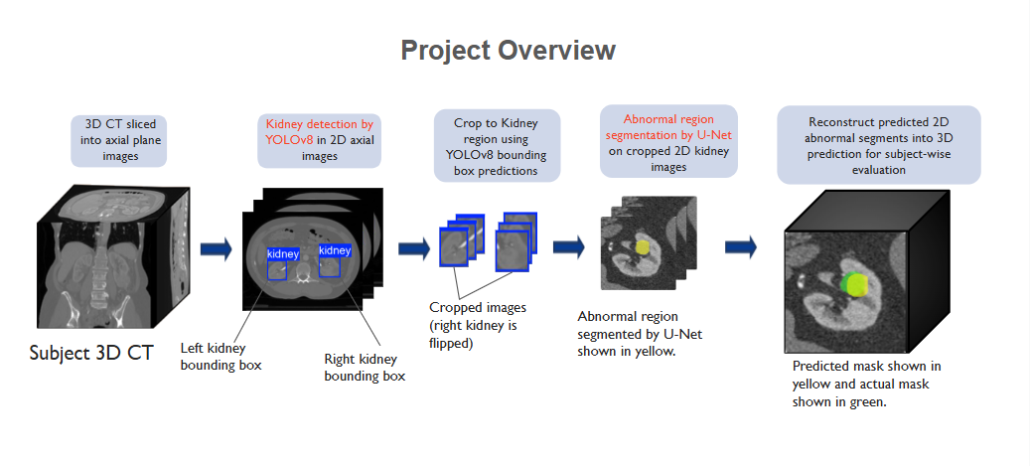
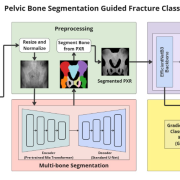
CSE424: Neural Network
| Weeks | Topics | Lectures | Presentation Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Week-1 | Neural Network Basics, Multilayer Perceptron, Linear Classifiers, Loss calculation, Log likelihood loss, Cross Entropy Loss, Softmax Classifier, Different Activation Functions and their Derivatives | 2 | |
| Week-2 | Gradient Descent, Chain Rule for Derivatives, Back Propagation, Update Rule, Implementation of Multilayer Perceptron from Scratch that uses back propagation | 2 | |
| Week-3 | Convolutional Neural Network, Filters, Kernels, Convolutional Layer, Max Pool Layer, Activation Function ReLU, Batch Normalization, Implementation of CNN from Scratch | 2 | |
| Week-4 | Capacity, Overfitting, Under fitting, Regularization, Weight Decay, Dropout, Batch Normalization, Convolutional AutoEncoder, Semantic Segmentation, Different up-sampling method (Deconvolution, Reverse Maxpool) | 2 | Presentation: Semantic Segmentation Presentation 1. Segnet 2. FCN-8 |
| Week-5 | Attention, Where CNN pays attention for classification Concept: Class Activation Map (CAM) | 2 | 1. GradCAM Learn to Pay Attention |
| Week-6 | Object Detection, Object localization , Region Proposal, Regional Convolutional Neural Network (R-CNN) , Mask R-CNN | 2 | 1. YOLO 2.Fast R-CNN 3.Faster R-CNN |
| Week-7 | Word Embedding, Word2vec, Negative Sampling, Character Level Embedding, Sentence Level Embedding | 2 | 1. Attention all you need 2. BERT |
| Week-8 | LSTM/GRU for language model, Neural Machine Translation, LST/GRU + Attention, Image Captioning | 2 | 1. Show, Attend, and Tell |
| Week-9 | Self-Attention, Transformer for Neural Machine Translation | 2 | 1. Transformer-XL |
| Week-10 | Introduction to Graph Embedding, Node2vec, Graph Convolution Network | 2 | 1. Representation Learning on Graphs: Method and Application |
| Week-11 | Graph Neural Network (GNN) style Embedding, Graph Attention Network (GAT) style embedding | 2 | 1. GraphSage |
| Week-12 | Advanced Topics Variational Auto Encoder, Generative Adversarial Network, Few/Zero Shot Learning | 2 |